Web UI REST Basics
Overview
This tutorial will show you the basics of how to implement and use a REST-based user interface (UI).
We'll concentrate here on the basics of a UI based on a RESTful API, for the details on initializing and setting up an HTTP server, parsing, headers, and more details on the API, please check the HTTP server tutorial.
Build and try
Follow the Build Tools tutorial to setup your development environment.
Start a terminal in the project directory; if you've not already done so, clone the Mongoose Library repo
git clone https://github.com/cesanta/mongooseBuild and run the example
cd mongoose/tuforials/webui/webui-rest make clean allGo to
http://localhost:8000in your browser- Click on "Call F1", see the results in the log
- Click on "Call SUM(1,2)", see the results in the log
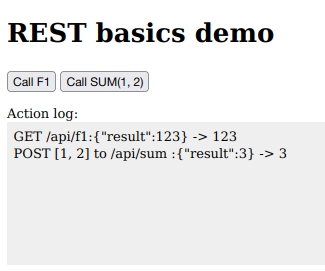
The button on the left sends an HTTP request using the GET method to the URI
/api/f1and shows the results, we can simulate that manually by connecting to the REST API with curl, for example:curl localhost:8000/api/f1 {"result": 123}The button on the right sends an HTTP request using the POST method to the URI
/api/sum, containing a JSON array[1, 2]in the BODY; then shows the results. We can simulate that manually by connecting to the REST API with curl, for example:curl localhost:8000/api/sum -d '[123, 456]' {"result":579}
Backend implementation
When we get an HTTP request, we must gather more information about it. First, we cast the function argument
ev_datato a struct mg_http_message, which contains a parsed HTTP request. Then, we check the URI by calling mg_match().If the HTTP request is for the
/api/f1URI, we serve a response using mg_http_reply(), that allows us to generate responses with specific headers and body. It simply prints data to the connection's output buffer according to aprintf()-like format specification; it is a convenient wrapper around the functionmg_printf(), that adds a correct status message and aContent-Lengthheader. The identifier m and, through the macroMG_ESC(), function mg_print_esc(), are used to print double-quoted JSON-escaped strings.
- If the HTTP request is for the
/api/sumURI, we assume that the client has sent us the numbers to add as a JSON array in the POST body:[1, 2]. We fetch them using Mongoose's built-in JSON API, calculate the sum, and respond with a result. The function mg_json_get_num() will parse a JSON string in astruct mg_str, searching for a valid numeric value at the JSON pathpath. If successful, it will store its value at placeholdervand return true; returning false otherwise. Thebodyelement inside thestruct mg_http_messagewe got, is astruct mg_str; so we try to extract both values and if we succeed, we print a result.
Check the JSON-RPC tutorial for a more involved example of handling JSON.
You can also check tutorials/http/http-restful-server for an expanded version of this minimal example.
Frontend implementation
The JavaScript code in the browser gets the elements that are present on the page, then enables the buttons.
- On a "Call F1" button click, the code calls the
fetch()method to GET/api/f1, extracts the returned JSON object, turns it into a string and shows it in the log
- On a "Call SUM(1,2)" button click, the code calls the
getsum()function and passes numbers 1 and 2 as parameters, then parses the JSON object returned bygetsum(), turns it into a string and shows it in the log.
- The function
getsum()calls thefetch()method to POST to/api/sumsending its arguments in the body as a JSON array; then extracts the JSON object returned by the backend, and returns it.















 Mongoose
Mongoose