Device dashboard - baremetal, using Keil MDK
Overview
This tutorial shows how to implement a Web device dashboard using Mongoose Library on STM32 Nucleo development boards, using the ARM Keil MDK development environment. We provide instructions for NUCLEO-F746ZG, NUCLEO-F429ZI.
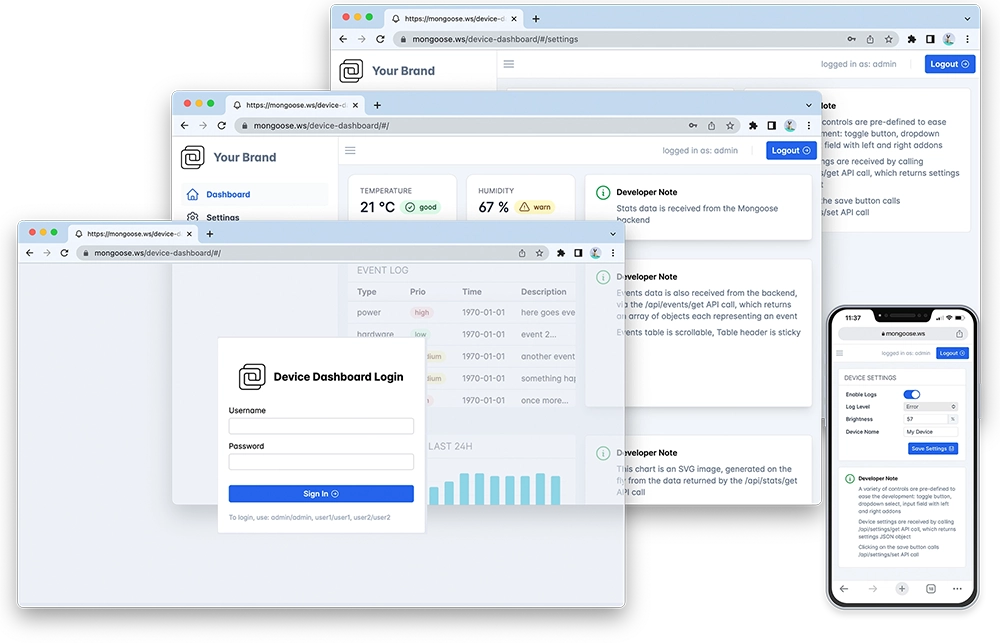
Features of this implementation include:
- Bare metal - uses no external frameworks / middlewares, except for the STM32Cube HAL, used for peripheral initialization
- Uses ARM CMSIS Core and device headers through Software Packs
- Uses Mongoose's built-in TCP/IP stack, which includes an STM32 Ethernet driver
- Does NOT use an external network stack like lwIP, or RTOS like FreeRTOS
- The Web dashboard provides:
- User Authentication: login protection with multiple permission levels
- The web UI is optimized for size and for TLS usage
- Logged users can view/change device settings
- The web UI is fully embedded into the firmware binary, and does not need a filesystem to serve it, making it resilient
This example is a hardware adaptation of the Device Dashboard that can run on Mac/Linux/Windows. Mongoose Library, being cross-platform, allows to develop and run the same code on different platforms. That means: all functionality related to networking can be developed and debugged on a workstation, and then run as-is on an embedded device - and this example is a demonstration of that.
Take your time to navigate and study the Device Dashboard tutorial. Here, we concentrate on the features specific to this embedded platform in the Keil MDK environment.
Though we specifically link to the files for a NUCLEO-F746ZG implementation, most references in this tutorial are valid for any supported board:
| Board | Files |
|---|---|
| NUCLEO-F429ZI | tutorials/stm32/nucleo-f429zi-keil-baremetal |
| NUCLEO-F746ZG | tutorials/stm32/nucleo-f746zg-keil-baremetal |
This example is a plain Keil MDK-based project with the following files of interest:
- main.c - provides the
main()entry point with hardware init, LED blinking and network init. - hal.h - provides an abstraction for MAC generation
- syscalls.c - provides a low level function to redirect debug output to a UART.
mongoose.c,mongoose.h- Mongoose Librarynet.c,net.h- part of the device dashboard example, contains the Web functionalitypacked_fs.c- part of the device dashboard example, embeds the Web UI used by the dashboard
All these files have been grouped in Source Group 1 in the Project Explorer. Keil MDK can integrate with STM32CubeMX, and we use it. The device configuration file, used as the recipe to generate the code for device initialization, is handled by the IDE, we access it through the Run-Time Environment manager. For all auto-generated files, we've used those places designated for USER_CODE, so all files can be re-generated by STM32CubeMX for newer versions of the firmware packs.
Below is a general process outline:
- The board IP addressing will be provided by a DHCP server. If you want to set a static configuration, set IP address, network mask and gateway in
main.c; see below - Build the example (see below) and run it on a development board
- The firmware initializes the network
- After initialization, the application starts Mongoose's event loop and blinks a blue LED
- Once the blue LED starts blinking, the example is ready
- Open your web browser and navigate to the board IP address, you should see a nice device dashboard
Build and run
Follow the Build Tools tutorial to setup your development environment.
In your project directory, clone the Mongoose Library repository using git
Start μVision and open the project; if you need a quick start on the ARM Keil MDK and μVision, follow this step by step tutorial.
In order to build this project, click the
Buildicon. To flash this firmware to your board, plug it in a USB port and click on theLoadicon. When finished, you have to reset your board pressing its reset button. You should soon see the blue LED start blinking. As long as there is only one board plugged in, μVision will find it; though we need to know the serial port device to be able to get the log information. You'll need to dig for it in your computer.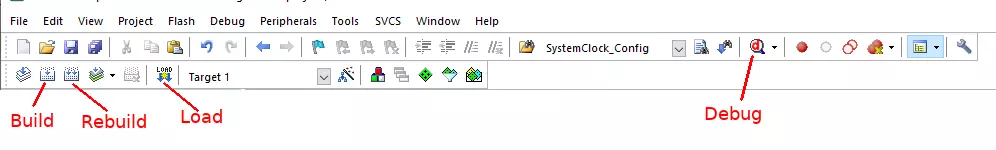
When the firmware starts, the board should signal its state by blinking the blue LED. We now need to know the IP address of the board to connect to it. If we used DHCP, as it is the default, we can check our DHCP server logs or see the device logs. Let's do this.
To connect to the board, in this example we'll be using PuTTY; we configure it for 115200bps.
8 2 main.c:144:main Starting, CPU freq 216 MHz e 2 main.c:160:main MAC: 02:35:42:56:22:2e. Waiting for IP.. ... adb 2 mongoose.c:7366:onstatechange READY, IP: 192.168.69.235 ae2 2 mongoose.c:7367:onstatechange GW: 192.168.69.1 ae7 2 mongoose.c:7369:onstatechange Lease: 21600 sec aed 2 main.c:165:main Initialising application... af4 3 mongoose.c:3356:mg_listen 1 0x0 http://0.0.0.0 af9 2 main.c:169:main Starting event loopNow start a browser on
http://IP_ADDRESS, whereIP_ADDRESSis the board's IP address printed on the serial console. You should see a login screen as in the image aboveFrom here on, if you want to try the dashboard features please go to the device dashboard tutorial and follow some of the steps depicted there.
Compilation options
MG_ARCH = MG_ARCH_ARMCC- configures Mongoose to work with the ARM Compiler version 6 in the Keil MDK environmentMG_ENABLE_CUSTOM_MILLIS = 1- lets the firmware code overridemg_millis()MG_ENABLE_CUSTOM_RANDOM = 1- lets the firmware code overridemg_random()to use the device hardware RNGMG_ENABLE_TCPIP = 1- enables the built-in TCP/IP stackMG_ENABLE_PACKED_FS = 1- enables the embedded filesystem support- To enable the proper built-in driver for your board:
Board Compilation option NUCLEO-F429ZI MG_ENABLE_DRIVER_STM32F = 1NUCLEO-F746ZG MG_ENABLE_DRIVER_STM32F = 1
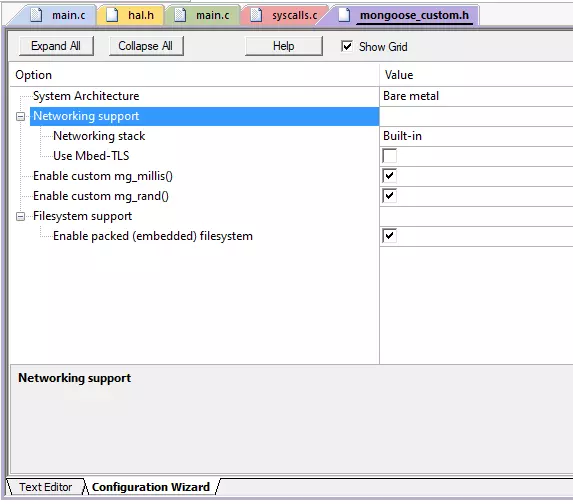
These are grouped in the file mongoose_config.h. This file has been written using scripting extensions, so you can just select the Configuration Wizard tab at the bottom of the editor to see the file contents in a friendly way.
main.c overview
This example can be divided in the following blocks:
- Provide a time base in milliseconds and take advantage of the true RNG in the microcontroller
- Initialize the microcontroller for this particular board
- Initialize Mongoose
- Initialize the networking stack
- Run Mongoose
Custom mg_millis()
Network operations need a time base to calculate timeouts. Mongoose supports a number of well-known architectures, but since here we are working at the bare-metal level, we need to provide our own custom function. The necessary actions are:
- Define
MG_ENABLE_CUSTOM_MILLIS=1which is done inmongoose_config.h - Provide a custom
uint64_t mg_millis(void)function:
As you can see, we take advantage of the Cube HAL and just call its timing function
Custom mg_random()
Some network operations require the generation of random numbers, from simple port numbers that should be different on every reset to complex TLS operations. Mongoose supports a number of well-known architectures, but since here we are working at the bare-metal level, we need to provide our own custom function or default to the standard pseudo-random number generator. The necessary actions are:
- Define
MG_ENABLE_CUSTOM_RANDOM=1which is done inmongoose_config.h - Provide a custom
void mg_random(void *buf, size_t len)function:
In this example, this function uses the microcontroller's built-in RNG through the STM32Cube HAL
MCU and board initialization
Microcontroller support is provided by Keil firmware packs, which are based on STM32Cube firmware packages. The microcontroller, its clock, and all peripherals we use are initialized by HAL functions according to the configuration, code like this is generated by STM32CubeMX. In fact, to reproduce all the configuration steps, follow the step by step tutorial up to and including step 5. In particular, step 1 describes the additions we need to do to a Cube-generated main file to call the generated initialization functions, this mx_init() function we call at the start of our main() function:
Since this is a baremetal project but we do not control everything, to be on the safe side we've setup some room for the stack and some for the heap. This is done at project creation, and can be seen by opening the assembly startup file (Device/startup_<devicefamilyname>.s) in μVision and use the Configuration Wizard. This setting affects the linker process.
Mongoose initialization
Then we initialize Mongoose, this is no different from what we always do in any example.
There is also a timer that we use to blink the blue LED and output some status information:
For more information on timers, check the timers tutorial.
TCP/IP initialization
The built-in TCP/IP stack has to be enabled to be compiled in, and so Mongoose will work in association with it. This is done in mongoose_config.h by defining MG_ENABLE_TCPIP=1.
Then this networking stack has to be configured and initialized. This is done by calling mg_tcpip_init() and passing it a pointer to a struct mg_tcpip_if. Inside this structure:
- have pointers to a
struct mg_tcpip_driverand any extra data that it could need - For DHCP: set
ipas zero - For a static configuration, specify
ip,mask, andgwin network byte order
In this example we use DHCP, but you can remove the comments and set a static configuration if you want:
Note that, we also need to specify a unique MAC address; this example provides a macro to transform the chip built-in unique ID into a unicast locally administered address; for production runs you'll have to consider among several options, from adding a MAC address chip in your hardware design to registering with the IEEE Registration Authority.
Some drivers, as you have probably noticed, require extra data. In this case the STM32 driver can accept the setting for the divider that generates the MDIO clock. You can pass a null pointer in the driver data or a negative value for this parameter and the driver will calculate it for you, based on the clock configuration.
Run Mongoose
Then we run Mongoose. This is no different from what we always do in any example, though note that it should be run after network initialization. The logic is standard: initialize the event manager (as we already did), start a listener, and fall into an infinite event loop:
In this case, the listener is started by web_init(), the device dashboard initialization function. The URL is configured by the macro HTTP_URL, which we set in the Makefile.
We have covered those aspects that are specific to the STM32 implementation, for the details on the application and the UI, please see the Device Dashboard tutorial.















 Mongoose
Mongoose